La urbanización del litoral alicantino: un modelo urbano insostenible, vulnerable a la sequía y a los efectos del cambio climático
Palabras clave:
Vulnerabilidad, Urbanización, Agua, Sequía, Cambio climático, AlicanteResumen
El litoral de Alicante (sureste español) ha sufrido importantes transformaciones territoriales (urbanización extensiva, incremento del número de viviendas y población) desde mediados del pasado s. XX. A ello, cabe sumar la aridez natural propia de la región y efectos de las sequías y su aseveración según los escenarios del cambio climático. Los objetivos de esta investigación son analizar cómo se ha producido la urbanización en la costa de Alicante, poner de manifiesto cuál es la principal tipología urbana implantada y relacionar el gasto de agua de ésta con el resto de tipologías. Metodológicamente se han consultado diferentes documentos y fuentes sobre cambio climático, recursos hídricos, demandas y evolución de usos del suelo urbano. Los resultados ponen de manifiesto que este territorio ha acrecentado su grado de vulnerabilidad frente a la sequía debido a la implantación de una tipología urbana (chalés) caracterizada por una alta demanda de agua. Todo ello cobra mayor interés si se tienen en cuenta los efectos del cambio climático que prevén una mayor intensidad y duración de los periodos de sequía en la región mediterránea.
Descargas
Descargas
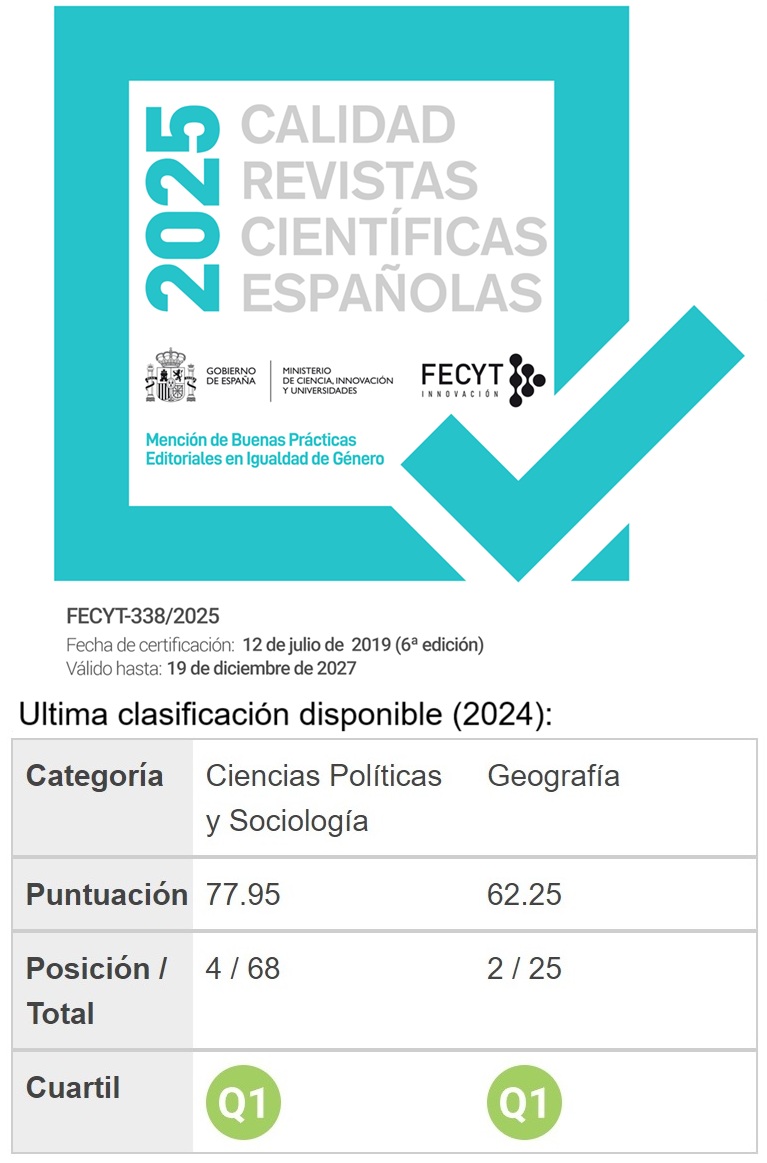
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2019 Álvaro Francisco Morote-Seguido, María Hernández-Hernández

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Sin perjuicio de lo dispuesto en la legislación vigente sobre Propiedad Intelectual, y conforme a la misma, el/la los/las autor/a/es/as que publiquen en CyTET cede/n a título gratuito, de modo no exclusivo y sin límite temporal al Ministerio de Transportes, Movilidad y Agenda Urbana los derechos para difundir, reproducir, comunicar y distribuir en cualquier formato actual o futuro, en papel o electrónico, la versión original o derivada de su obra bajo licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), así como para incluir o ceder a terceros la inclusión de su contenido en índices, repositorios y bases de datos nacionales e internacionales, con referencia y reconocimiento en todo caso de la autoría del mismo.
Además, al realizar el envío, el/la los/las autor/a/es/as declara/n que se trata de un trabajo original en el que se reconocen las fuentes que han sido utilizadas en su estudio, comprometiéndose a respetar la evidencia científica y a no modificar los datos originales para verificar o refutar una hipótesis de partida; que el contenido esencial del mismo no ha sido publicado previamente ni se publicará en ninguna otra obra o revista mientras esté en proceso de evaluación en la revista CyTET; y que no se ha remitido simultáneamente a otra publicación.
Los autores deben firmar un Formulario de Cesión de Derechos, que les será enviado desde la Secretaría de CyTET una vez se acepte su artículo para ser publicado.
Con el objetivo de favorecer la difusión del conocimiento, CyTET se adhiere al movimiento de revistas de Open Access (OA) y entrega la totalidad de sus contenidos a diversos índices, repositorios y bases de datos nacionales e internacionales bajo este protocolo; por tanto, la remisión de un trabajo para ser publicado en la revista presupone la aceptación explícita por parte del autor/a de este método de distribución.
Se anima a las/os autoras/es a reproducir y alojar sus trabajos publicados en CyTET en repositorios institucionales, páginas web, etc. con la intención de contribuir a la mejora de la transferencia del conocimiento y de la citación de dichos trabajos.






 Enlace a CyTET en Linkedin
Enlace a CyTET en Linkedin